Key Features
- SaltStick® Vitassium is a medical food specifically formulated to provide sodium and potassium for the clinical dietary management for patients with autonomic dysfunction including Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS), Ehlers Danlos Syndrome (EDS), Cystic Fibrosis (CF), and Vasovagal Syncope, when increased plasma volume has been shown to be beneficial.
- Vitassium helps to maintain electrolyte levels, to support healthy blood pressure, and to reduce fatigue and dizziness due to low blood pressure.
- Made in the USA at cGMP facility. Learn more about our manufacturing and safety.
- Each serving (2 capsules) contains: 500 mg sodium (22 mmol sodium, 1270 mg sodium chloride), 100 mg potassium.
- Tasteless capsules are small (size 0) and easy on the stomach.
- Vitassium is non-GMO, vegan, gluten free, preservative free, allergen free, starch free.
- Ingredients: Sodium chloride, potassium citrate, vegetarian stearic acid, vegetable capsule. Learn more about our ingredient list.
- Suggested use: As a medical food, take one to two (1-2) capsules with water, three to four (3-4) times a day, for up to ten (10) capsules daily. View our Vitassium Usage Guide.
- Available in 8ct daily-use packets and 100ct bottles.
- SHOP NOW: USA shopsaltstick.com, and Canada thepodiumshop.ca, and the UK shopsaltstick.co.uk
Why Choose Vitassium?
SaltStick® Vitassium is specifically formulated to provide sodium and potassium for the clinical dietary management for patients with autonomic dysfunction including Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS), Ehlers Danlos Syndrome (EDS), Cystic Fibrosis (CF), and Vasovagal Syncope, when increased plasma volume has been shown to be beneficial. Vitassium helps to maintain electrolyte levels, to support healthy blood pressure, and to reduce fatigue and dizziness due to low blood pressure.
- Clean & Simple Ingredients — get the full list of ingredients in SaltStick Vitassium and learn how SaltStick Electrolytes are manufactured and tested.
- Community Sponsorship — learn about SaltStick's partnership with Dysautonomia International and U.S.-based physicians, plus learn how the Vitassium Club can save you money.
- Detailed Usage Guide — learn how to use SaltStick Vitassium as a medical food
- Backed by Research—learn the science behind SaltStick Vitassium on our dysautonomia and POTS medical research page.
- Answers to Your FAQ — the most frequently asked questions about SaltStick Vitassium. Topics include product purchases, usage, safety, partnerships, expiration and warranty.
Clean & Simple Ingredients
SaltStick Electrolytes made in the USA at an FDA-inspected cGMP (current Good Manufacturing Practices) facility. Learn more about our manufacturing and safety standards. All ingredients in SaltStick Vitassium are clearly labeled on the bottle. Click on the label below to view a larger image.
Community Sponsorship
SaltStick is proud to support the POTS and dysautonomia communities through our partnership with Dysautonomia International and our consumer Vitassium Club. A portion of all proceeds from Vitassium sales are donated to Dysautonomia International to help promote dysautonomia awareness and research. Individuals with dysautonomia, POTS or EDS that use SaltStick as a medical food are welcome to apply for the Vitassium Club to get the best price on Vitassium and other SaltStick Electrolytes when they order at shopsaltstick.com.

Did you know? SaltStick partners with Dysautonomia International to help support funding for dysautonomia research.
In July 2016, SaltStick announced our partnership with Dysautonomia International. We pledged to donate to Dysautonomia International 10% of all SaltStick Vitassium sales, which is specifically designed to help supply buffered sodium and potassium in a small stomach-friendly capsule. Donations exclusively fund research, patient awareness, and patient and family support.
Join the Vitassium Club!
 The Vitassium Club is strictly for individuals with dysautonomia, POTS or EDS that use SaltStick as a medical food. If this describes you, or a child or dependent you care for, then we encourage you to join the Vitassium Club today.
The Vitassium Club is strictly for individuals with dysautonomia, POTS or EDS that use SaltStick as a medical food. If this describes you, or a child or dependent you care for, then we encourage you to join the Vitassium Club today.
-
-
- Vitassium Club members get the best price on Vitassium and other SaltStick Electrolytes when they order at shopsaltstick.com. No need to enter coupons or promos at checkout!
- Vitassium Club members are the first to know about new medical literature, special promotions and new products.
- Join the Vitassium Club today!
-
SaltStick supports Physicians!
 SaltStick is proud to provide FREE Vitassium sample packets exclusively to qualified U.S. physicians and clinics. Through our Vitassium Physician’s Program, SaltStick offers to donate free Vitassium 8-count sample packets to U.S.-based physicians and clinics who care for individuals with dysautonomia, POTS or EDS. Our Physician’s Program began in 2015 with the original SaltStick Caps product, and has since grown to many clinics and care facilities around the country. You can learn more about our Vitassium Physician's program here.
SaltStick is proud to provide FREE Vitassium sample packets exclusively to qualified U.S. physicians and clinics. Through our Vitassium Physician’s Program, SaltStick offers to donate free Vitassium 8-count sample packets to U.S.-based physicians and clinics who care for individuals with dysautonomia, POTS or EDS. Our Physician’s Program began in 2015 with the original SaltStick Caps product, and has since grown to many clinics and care facilities around the country. You can learn more about our Vitassium Physician's program here.
Detailed Usage Guide
Vitassium is intended for use under medical supervision. If you are an individual whose physician has recommended additional intake of salt (sodium), SaltStick Vitassium may be helpful to increase your electrolyte intake in a simple capsule format. With easily-quantified dosing of 250mg sodium (635mg salt, 11 mmol) per capsule, it makes it easy to take just the right amount for the desired intake. Vitassium also contains potassium in a 5:1 ratio that provides a balanced intake of both major blood electrolytes. Potassium citrate also acts as a buffering agent to minimize pH changes in the blood, and can help soothe the stomach.
Vitassium comes in smaller, size "0" vegetarian capsules that are easy to eat and easy on the stomach, especially as compared with salt (sodium chloride) tablets. Capsules should be consumed with water.
What Vitassium doesn't have also matters. Vitassium is made from non-GMO ingredients, and is vegan, gluten free, preservative free, allergen free, and starch free.
It is often recommended to increase both fluid and salt intake in order to increase blood volume, which is typically low in POTS patients. This has been shown to be particularly helpful in patients with blood pooling, hypovolemia, or hypotension.1 Except for the hyperadrenergic subtype of POTS, a fluid intake of approximately two liters and an intake of three to five grams of salt is often recommended per day2.
Every individual will have a different "ideal" usage and dosage. We strongly encourage you to consult with your physician on what may work best for you. To assist with making the association between salt intake and Vitassium intake easier, we have prepared the following table:
For example, if your doctor suggests taking 4g (4000mg) salt per day, that would equal 6-7 Vitassium capsules. To reduce the chance of stomach irritation, we suggest spreading out the dosage in 3-4 smaller doses throughout the day. For example, 2 capsules per serving, taken 4x per day would provide 5g of salt, or 2000mg sodium.
If you are using other products containing sodium, be sure to compare sodium values or sodium chloride values against each other, and remember that the two values are not equal. It is also worth noting that 1 Vitassium capsule (250mg Na) equals 11mmol sodium, which is another unit of measure sometimes seen on products containing sodium.
SaltStick Vitassium is designated as a medical food, as defined in 21 U.S.C. 360ee (b) (3) as a food which is formulated to be consumed under the supervision of a physician and which is intended for the specific dietary management of a disease or condition for which distinctive nutritional requirements, based on recognized scientific principles, are established by medical evaluation.
1) Abed, Howraa, Patrick A. Ball, and Le-Xin Wang. "Diagnosis and Management of Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome: A Brief Review." Journal of Geriatric Cardiology 9 (2012): 61-67.
2) Grubb, Blair P. "Postural Tachycardia Syndrome." Circulation: Journal of the American Heart Association 117 (2008): 2814-817.
Backed by Research
Toker Engineering has been a leading supplier and expert on electrolytes for over 10 years. SaltStick products have been trusted by some of the top professional athletes in the world and have been present on many of the top competitive world stages over the years. SaltStick has been to the top of Mt. Everest, and around the globe. Rigorous and self-imposed testing standards for SaltStick products exceed government requirements. Manufacturing occurs at a fully-certified site in the USA, from local ingredients whenever possible, all of the highest pharmaceutical quality. SaltStick has been trusted by doctors who feel their patients would benefit from additional intake of electrolytes.
Vitassium is SaltStick's improved solution to ongoing demand for a potent sodium source that is easy on the stomach, in a compact vegetarian capsule. To help more people, we have partnered with Dysautonomia International, the non-profit dedicated to funding research and information on autonomic diseases, including POTS (Postural Orthostatic Tachacardia Syndrome) and EDS (Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome).
Based on extensive research (some of the links appear below) and discussions with physicians who specialize in cardiology and pediatric medicine, Vitassium was formulated with just a few simple ingredients: sodium chloride and potassium citrate in a vegetarian capsule, with a tiny amount of stearic acid (*naturally present in many foods) added as a processing agent. Feedback from patients using SaltStick Caps reinforced the capsule format as stomach-friendly. Reducing the capsule size allows smaller individuals to consume the capsule, with fluid, more easily than the larger SaltStick Caps product.
Additional Reference & Reading Links:
- Lifestyle adaptations for people with POTS.
- Abed, Howraa, Patrick A. Ball, and Le-Xin Wang. “Diagnosis and Management of Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome: A Brief Review.” Journal of Geriatric Cardiology 9 (2012): 61-67.
- Grubb, Blair P. “Postural Tachycardia Syndrome.” Circulation: Journal of the American Heart Association 117 (2008): 2814-817.
- Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS) (Koichi Mizumaki MD PhD)—PDF Link
- Salt Supplementation Improves Orthostatic Cerebral and Peripheral Vascular Control in Patients With Syncope (Victoria E. Claydon, Roger Hainsworth)—PDF Link
- Orthostatic Hypotension in the Elderly: Diagnosis and Treatment (Vishal Gupta, MD, PhD, Lewis A. Lipsitz, MD)—Summary; PDF Link
- Treatment of Neurally Mediated Reflex Syncope (Juan C. Guzman, MD, Luciana V. Armaganijan, MD, Carlos A. Morillo, MD)—Summary; PDF Link
- Take a Stand: A neurologic disorder known as POTS causes dizziness and fainting—and frustration, due to lack of awareness and inadequate treatment (Amy Paturel)—Summary; PDF Link
- Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome: The Mayo Clinic Experience (Mark J. Thieben, MD et al)—Summary; PDF Link
- Postural Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS) (Phillip A. Low, M.D. et al)—Summary; PDF Link
- Low-sodium diet might not lower blood pressure—Summary; PDF Link
- Mild dehydration impairs cognitive performance and mood of men (Matthew S. Ganio, MD)—Summary; PDF Link
- Strategies for Ensuring Good Hydration in the Elderly (Monique Ferry, MD)—Summary; PDF Link
- Cardiac Origins of the Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (Qi Fu, MD, et al)—Summary; PDF Link
- Sodium and potassium intake and blood pressure change in childhood (Johanna M Geleijnse, Diederick E Grobbee, Albert Hofman)—Summary; PDF Link
- Dizziness and syncope in adolescence (Karen A McLeod)—Summary; PDF Link
- Salt supplement increases plasma volume and orthostatic tolerance in patients with unexplained syncope (H El-Sayed, R Hainsworth)—Summary; PDF Link
- Salt Supplementation Improves Orthostatic Cerebral and Peripheral Vascular Control in Patients With Syncope (Victoria E. Claydon, Roger Hainsworth)—Summary; PDF Link
- Hydration and Cognitive Function in Children (Kristen E. D’Anci et al)—Summary; PDF Link
What Customers Say:
“I’m on a high sodium diet to control super-low blood pressure, and Saltstick has been a lifesaver for me. The capsules dissolve quickly to give me a little boost of sodium without having to gag down liters of icky electrolyte drinks. They don’t cause any heartburn or stomach upset, and they don’t have a bunch of unnecessary ingredients (or calories!).” — Amazon reviewer Delilah
“I suffer from adrenal fatigue, which also takes the salt out of my body. I was given sodium pills to take twice a day. I could not take them with out becoming ill. I found [SaltStick] online, and they are a miracle to me. My sodium went up, they don’t make me sick, so this product helped.” — Amazon reviewer Debra Duboux
“I have POTS and this helps me so much! I highly recommended theses, especially if you exercise. It’s a capsule and a glass of water: easy to get down, and I didn’t have any problems with them.” — Amazon Customer
“All I can say is ‘Wow!’ I have Mitral Valve Prolapse Syndrome (MVPS), which sometimes goes by the abbreviation of POTS or Dysautonomia. When I take these, not only do I feel so much better, but my workouts have been literally twice as effective: I can run longer and bike longer, all while feeling 10 times less fatigue and pain in my muscles that used to be caused by lack of blood flow and lack of electrolytes.” — Amazon Reviewer Daniel
“My daughter uses these to supplement her salt intake. She takes 3-5 a day and has no issues with stomach upset. She has POTS and needs to consume 4,000 -5,000 mg of sodium daily.” — Amazon Reviewer Nora
SaltStick Vitassium — FAQ
Below is a list of the most frequently asked questions specifically about SaltStick Vitassium.
Please note: for a full list of frequently asked questions, please visit our FAQ page.
1. What is Vitassium?
2. My doctor told me to take salt tablets. Does that mean just salt?
3. Why use Vitassium rather than SaltStick Caps or Fastchews?
4. Is it standard for "salt tablets" to contain other electrolytes?
5. My doctor suggested I take x grams of salt per day. How many Vitassium capsules should I consume?
6. Can Vitassium be consumed on an ongoing daily basis?
7. Should I take Vitassium alone without balancing other electrolytes?
8. Will taking this product long term cause other electrolyte imbalances?
9. Does Vitassium upset the stomach?
10. Why is there potassium in Vitassium capsules?
11. Do we disclose label and all ingredients?
12. Do you offer free samples?
13. Vitassium is expensive. Are there cheaper options?
14. Is Vitassium for athletes? What is the difference between Vitassium and other SaltStick products?
15. Are Vitassium capsules the same size as SaltStick Caps?
16. What type of allergens are present in Vitassium? Is there corn, soy, etc?
17. Does Vitassium contain caffeine?
18. What are the ingredients in Vitassium?
19. Why is there vegetarian stearic acid? Is that safe?
20. Are the vegetable capsules really made from vegetables?
21. How many Vitassium capsules should I take?
22. How should Vitassium capsules be stored?
23. Do Vitassium capsules expire?
24. What if I have further questions or comments?
25. What does Vitassium have to do with Dysautonomia International?
26. Is Vitassium a drug? Do I need a prescription to purchase Vitassium?
27. Is Vitassium purchase allowable under my insurance or FSA account?
28. Is Vitassium cGMP? What kind of facility produces Vitassium?
29. Can you send samples to my doctor for other patients to try?
30. Is Vitassium vegan?
SaltStick Vitassium is specifically formulated to provide sodium and potassium as part of the dietary management for patients with autonomic dysfunction including Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS), Ehlers Danlos Syndrome (EDS), Cystic Fibrosis (CF), and Vasovagal Syncope, when increased plasma volume has been shown to be beneficial. Vitassium helps to maintain electrolyte levels, to support healthy blood pressure, and to reduce fatigue and dizziness due to low blood pressure.
2. My doctor told me to take salt tablets. Does that mean just salt?
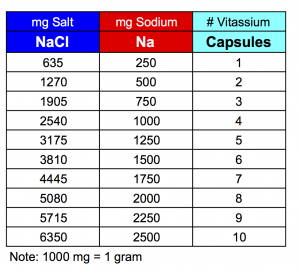
"Salt" is usually considered to be Table Salt, which is chemically known as Sodium Chloride. By weight, sodium chloride contains about 40% sodium. Nutrition information on foods is always indicated as the mineral sodium. For example, 1 gram of salt (1000 milligrams) contains 400 mg of sodium. If your physician suggests taking 1g of salt, then you can consume either 1g of table salt, or 400mg of sodium as indicated on food labels. Vitassium contains 250mg of sodium per capsule, or 500mg sodium per 2 capsule serving. This equals 635mg salt per capsule or 1270mg salt per 2 capsule serving. Consult our chart below for more information.
3. Why use Vitassium rather than SaltStick Caps or Fastchews?
Vitassium was formulated specifically as a medical food for individuals seeking to increase sodium intake under physician supervision. SaltStick Caps and Fastchews were formulated for athletes seeking to replace electrolytes lost in sweat, which includes significant amounts of sodium and potassium. However, we recommend using the product that was engineered for the specific purpose, although both products can be used together if desired. Vitassium capsules are also more concentrated and smaller, making them easier to consume than SaltStick Caps, especially for smaller individuals.
4. Is it standard for "salt tablets" to contain other electrolytes?
"Salt" tablets usually contain only sodium chloride, common table salt. The salt is commonly mined or harvested from salt water, and then purified. Trace quantities of other minerals, such as potassium, manganese, zinc and others can be found in natural sources of salt, but the quantities are so small that in the context of a normal diet, are not necessarily helpful. Vitassium contains purified sodium chloride (salt) that is 99.9% pure. Vitassium also contains significant potassium, that helps balance the electrolyte content in the body, between plasma and inside cells. Most salt tablets do not contain potassium.
5. My doctor suggested I take x grams of salt per day. How many Vitassium capsules should I consume?
1 gram of salt (1000 milligrams) contains 400 mg of sodium. Vitassium contains 250mg of sodium per capsule, or 500mg sodium per 2 capsule serving. This equals 635mg salt per capsule or 1270mg salt per 2 capsule serving. See Vitassium FAQ #2 for more details.
6. Can Vitassium be consumed on an ongoing daily basis?
Yes, given the safety profile of the common and safe ingredients, sodium chloride and potassium citrate, as part of a normal diet and with regular hydration, ongoing use as a daily medical food should be well tolerated. If you have specific concerns, please consult with your physician.
7. Should I take Vitassium alone without balancing other electrolytes?
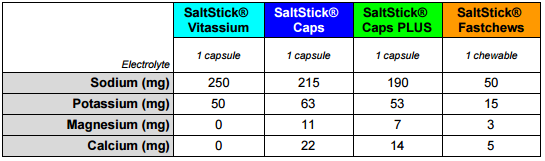
Vitassium contains a concentrated balance of buffered sodium and potassium. Other electrolyte intake through a normal and varied diet are necessary for proper mineral intake. For the purpose of electrolyte supplementation, the Vitassium composition is ideal. For athletes, we recommend SaltStick Caps or Caps Plus that contain magnesium and calcium in addition, in line with electrolyte losses by sweating.
8. Will taking this product long term cause other electrolyte imbalances?
Vitassium contains a balanced mixture of sodium and potassium. If you have any specific individualized concerns on electrolyte balance, please consult with your physician.
9. Does Vitassium upset the stomach?
Vitassium has been shown to be easy on the stomach according to our testers and long history of use by the similar SaltStick Caps product. Unlike salt tablets that can cause point-irritation in the stomach, capsules cause less stomach distress. Of course, individual results may vary.
10. Why is there potassium in Vitassium capsules?
Potassium is critical in the body for a variety of biochemical processes. One important function of potassium is to regulate the balance of water between plasma (blood) and within the cell. Providing sufficient building blocks for the body to self-regulate can be important. Vitassium contains an appropriate amount of potassium to assist in that regard. In general, excess potassium would be excreted in the urine.
11. Do we disclose label and all ingredients?
Of course. Ingredients are only and exactly: sodium chloride, potassium citrate, vegetarian stearic acid, vegetable capsule. Learn more about our ingredients here.
12. Do you offer free samples?
Sorry, but we currently do not offer free samples. We suggest you try a bottle, and you won't be disappointed. Customer feedback has been overwhelmingly positive and we are confident you'll agree. We do have a Physician Program that may be of interest. See Vitassium FAQ #29 for more details.
13. Vitassium is expensive. Are there cheaper options?
Join the Vitassium Club for exclusive discounts and pricing for those using Vitassium for medical conditions on a regular basis.
14. Is Vitassium for athletes? What is the difference between Vitassium and other SaltStick products?
Vitassium is not designed for athletes. Lacking other essential minerals commonly lost in sweat, magnesium and calcium, Vitassium was formulated for individuals who are seeking to increase their intake primarily of sodium, under the guidance of their physician. Our other products, SaltStick Caps, SaltStick Caps Plus and SaltStick Fastchews are better options for athletes or those in hot conditions who lose a significant amount of sweat.
15. Are Vitassium capsules the same size as SaltStick Caps?
No. Vitassium capsules are smaller size "0" that are easier to consume than the larger SaltStick Caps size "00" capsules. Both products should be consumed with water.
16. What type of allergens are present in Vitassium? Is there corn, soy, etc?
Vitassium is non-GMO, vegan, gluten free, preservative free, allergen free, starch free.
17. Does Vitassium contain caffeine?
No. Ingredients are only: sodium chloride, potassium citrate, vegetarian stearic acid, vegetable capsule.
18. What are the ingredients in Vitassium?
Sodium chloride, potassium citrate, vegetarian stearic acid, vegetable capsule.
19. Why is there vegetarian stearic acid? Is that safe?
Stearic acid is used as a solid lubricant that's helpful during the encapsulation process. It is on the GRAS (Generally recognized as safe) list in the USA that has been used safely for many years in many products. In fact, chocolate contains a large amount of stearic acid naturally, as do other food products. It is present in a very small quantity in Vitassium. It is specifically sourced from a vegetarian source.
20. Are the vegetable capsules really made from vegetables?
Hypromellose is a solid, non-toxic cellulose material derived from plants (wood/cotton fiber). There is no starch or corn present. Hypromellose is suitable for those following vegan and vegetarian diets.
21. How many Vitassium capsules should I take?
As a medical food, you should follow your physician's recommendations. In general, take one to two (1-2) capsules with water, three to four (3-4) times a day, for up to ten (10) capsules daily.
CAUTION: Do not exceed the recommended dose unless advised by your physician. Consult a physician before using this product, especially if you are a pregnant or nursing mother, a child under 18, or an individual with a known medical condition. Individuals with hypertension, chronic renal insufficiency, diabetes, or those on a low potassium or low-salt diet should not use this product without physician guidance.
22. How should Vitassium capsules be stored?
Store contents in a cool (room temperature or below) and dry environment.
23. Do Vitassium capsules expire?
Yes, the expiration date, as printed with the lot number on the bottom of the bottle or on the packet, is 3 years (bottle) or 4 years (packet) from date of manufacture, based on stability studies, we can confirm that the mineral content (label claim) is within legal requirements within the validity date period, provided the product is stored as indicated.
24. What if I have further questions or comments?
Please visit our contact page.
25. What does Vitassium have to do with Dysautonomia International?
We established a relationship with Dysautonomia International in 2016 to help support their research efforts towards treatment of autonomic diseases, including POTS. For every Vitassium product sold, 10% of sales are donated to Dysautonomia International towards these research efforts. Dysautonomia International is a 501(c)3 non-profit organization to assist with research, patient support and public education of autoimmune diseases.
26. Is Vitassium a drug? Do I need a prescription to purchase Vitassium?
SaltStick Vitassium is designated as a medical food, as defined in 21 U.S.C. 360ee (b) (3) as a food which is formulated to be consumed under the supervision of a physician and which is intended for the specific dietary management of a disease or condition for which distinctive nutritional requirements, based on recognized scientific principles, are established by medical evaluation.
Physicians may write a prescription for Vitassium, however, no prescription is needed to purchase a medical food.
27. Is Vitassium purchase allowable under my insurance or FSA account?
Please check with your insurance or FSA administrator if medical foods are covered under your specific plan.
28. Is Vitassium cGMP? What kind of facility produces Vitassium?
Vitassium is produced in the USA at an FDA-inspected cGMP (current Good Manufacturing Practices) and food-registered facility. The highest standards that would relate to supplement, medical food, and drug production are followed. The SaltStick name is a guarantee of quality. Learn more about our manufacturing and safety standards.
29. Can you send samples to my doctor for other patients to try?
Yes, please contact us with your doctor's information and our team will reach out to them.
30. Is Vitassium vegan?
Vitassium is non-GMO, vegan, gluten free, preservative free, allergen free, starch free.
Summaries of Research Articles
A Summary of Selected Scientific Research, References and Reviews Relating to Sodium Supplementation in POTS, EDS and Elderly Orthostatic Intolerance.
Jonathan Toker, Ph.D.
Healthy, free-living individuals can achieve sodium balance through normal diet alone. It is recognized that, on average, people with Western-style diets already consume sufficient (or excess) sodium. It is the purpose of SaltStick Vitassium to supply additional dietary sodium to specific populations who may benefit from higher sodium intake than average. In many cases, consumers seek to increase sodium intake as a first-line attempt to resolve certain underlying symptoms relating to high sodium excretion or poor sodium retention that is characteristic of conditions such as Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS), Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) and Cystic Fibrosis (CF), often under the recommendation and guidance of their physician as a first line non-drug treatment along with additional fluid intake, exercise and other lifestyle changes.
Additional sodium intake can also be of benefit for certain people to assist with proper hydration. In the absence of sodium replacement, intake of fluid is associated with a decrease in thirst and an increased diuresis despite the continued presence of a significant fluid deficit. In combination with increased salt intake, proper hydration is key to preventable and treatable fluid imbalance.
The following references are available as hyperlinks below, and major bullet points relating to the implementation of sodium supplementation are outlined for each article.
Gupta, Vishal, and Lewis A. Lipsitz. "Orthostatic hypotension in the elderly: diagnosis and treatment." The American journal of medicine 120.10 (2007): 841-847.
- Orthostatic hypotension is a common problem among elderly patients, associated with significant morbidity and mortality. While acute orthostatic hypotension is usually secondary to medication, fluid or blood loss, or adrenal insufficiency, chronic orthostatic hypotension is frequently due to altered blood pressure regulatory mechanisms and autonomic dysfunction. Previous studies have revealed an increased prevalence of orthostatic hypotension with age. In community dwelling individuals _65 years of age, its prevalence is approximately 20%; in those _75 years of age it is as high as 30%. In frail elderly individuals living in nursing homes, the prevalence of orthostatic hypotension is even higher, up to 50% or more.
- Orthostatic hypotension may be symptomatic or asymptomatic. However, even in asymptomatic patients it remains a risk for future falls and syncope, and should therefore be minimized as much as possible. Common symptoms at all ages include dizziness, light headedness, weakness, syncope, nausea, paracervical pain, low back pain, angina pectoris, and transient ischemic attacks. In elderly people, disturbed speech, visual changes, falls, confusion, and impaired cognition are more commonly seen
- Nonpharmacologic Treatment Options for Orthostatic Hypotension: Increase salt and water intake
- Liberal intake of salt and water to achieve a 24-hour urine volume of 1.5 to 2 liters may attenuate fluid loss commonly seen in autonomic insufficiency.
Guzman, Juan C., Luciana V. Armaganijan, and Carlos A. Morillo. "Treatment of neurally mediated reflex syncope." Cardiology clinics 31.1 (2013): 123-129.
- Several nonpharmacologic therapies have been developed, which include...salt and fluid intake.
- Simple measures, such as increased water and NaCl intake, should be routinely implemented as first-line therapy
Paturel, Amy. "Take a Stand: A neurologic disorder known as POTS causes dizziness and fainting—and frustration, due to lack of awareness and inadequate treatment." Neurology Now 11.1 (2015): 44-47.
- It’s estimated that between 1 and 3 million Americans are affected by the syndrome.
- POTS can strike at any age, but it primarily affects women between the ages of 15 and 50
- Salt helps the body retain water, which in turn increases blood volume.
- Drinking more fluids, especially in combination with salt, helps expand blood volume and increase blood flow. Most doctors recommend two to three liters per day of hydrating fluids such as vegetable or tomato juice, coconut water, decaffeinated tea with salt, or chicken broth.
Thieben, Mark J., et al. "Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome: the Mayo clinic experience." Mayo Clinic Proceedings. Vol. 82. No. 3. Elsevier, 2007.
- POTS is a relatively common condition
- An important first step in the assessment and treatment of patients with POTS is to determine their volume status and institute salt and fluid replacement in those with hypovolemia.
Low, Phillip A., et al. "Postural tachycardia syndrome (POTS)." Journal of cardiovascular electrophysiology 20.3 (2009): 352-358.
- POTS is defined as the development of orthostatic symptoms associated with a heart rate (HR) increment ≥30, usually to ≥120 bpm without orthostatic hypotension. Symptoms of orthostatic intolerance are those due to brain hypoperfusion and those due to sympathetic overaction.
- Patients with POTS require a high salt diet, copious fluids, and postural training.
- The hypovolemic patient will do well with expanding plasma volume with generous salt intake and fludrocortisone. The salt intake should be between 150–250 mEq of sodium (10–20 g of salt). Some patients are intensely sensitive to salt intake and can fine-tune their plasma volume and BP control with salt intake alone
- The patient should have at least 1 glass or cup of fluids with their meals and at least 2 at other times each day to obtain 2–2.5 L/day.
- Management always involves expansion of plasma volume with high salt and high fluid intake.
Lynn Moore (Boston University School of Medicine), Martha Singer (Boston University School of Medicine), M. Loring Bradlee (Boston University School of Medicine). "Low-sodium diet might not lower blood pressure" Experimental Biology 2017.
https://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2017-04/eb2-ldm041217.php
- There is no evidence that a diet lower in sodium had any long-term beneficial effects on blood pressure.
- All participants started with normal blood pressure readings, and participants who consumed less than 2,500 milligrams of sodium a day had higher blood pressure than participants who consumed higher amounts of sodium.
- High blood pressure (HBP) is a major modifiable risk factor for cardiovascular disease. To reduce blood pressure, current U.S. Dietary Guidelines recommend limiting sodium intake to 2.3 g/day for healthy individuals under the age of 50, while adults over age 50 as well as all African-Americans, and anyone with HBP, diabetes or chronic kidney disease is advised to limit sodium intake to 1.5 g/day. Very limited evidence is available to support these recommendations. Recent studies have called these guidelines into question and identified the need to consider the intakes of other minerals such as potassium, magnesium, and calcium in addition to sodium in relation to BP regulation.
- These long-term data from the Framingham Study provide no support for lowering sodium intakes among healthy adults to below 2.3 g/day as recommended.
- This study does support the finding of a clear inverse association between potassium, magnesium, and calcium and blood pressure change over time.
Ganio, Matthew S., et al. "Mild dehydration impairs cognitive performance and mood of men." British Journal of Nutrition 106.10 (2011): 1535-1543.
- Mild dehydration without hyperthermia in men induced adverse changes in vigilance and working memory, and increased tension/anxiety and fatigue.
- Individuals with medical conditions that increase susceptibility to dehydration such as diabetics, as well as children and elderly individuals, may be more likely to experience adverse behavioural effects of mild dehydration.
Ferry, Monique. "Strategies for ensuring good hydration in the elderly." Nutrition reviews 63.suppl 1 (2005): S22-S29.
- Extracellular dehydration, also called hypotonic hydration, is caused by a loss of sodium, leading to a proportional loss of water. Natremia is then low (<135 mmol/L), as is osmolality (<280 mOsm/L). Diuretic treatment resulting in salt loss is the main etiology. Hyponatremia is responsible for the increased morbidity and mortality associated with this type of dehydration.
- Those at risk for dehydration must drink abundantly, meaning that he or she must therefore be conscious and cooperative. Furthermore, the decrease of thirst perception and a thirst more quickly quenched often make it difficult to achieve sufficient liquid intake. It is therefore necessary to stimulate drinking using either low-osmolarity drinks such as water, broth, or sport drinks or high-osmolarity drinks such as carbonated, sugared drinks or fruit juices.
Fu, Qi, et al. "Cardiac origins of the postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome." Journal of the American College of Cardiology 55.25 (2010): 2858-2868.
- Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) (also called chronic orthostatic intolerance), in which patients are unable to stand or remain upright for prolonged periods because of intolerable light headedness, weakness, and near syncope. This disorder affects more than 500,000 Americans
- Patients were encouraged to increase their daily salt intake to 6 to 8 g/day and water intake to 3 to 4 l/day and to elevate the head of the bed during sleeping at night.
- It may be difficult to attribute the improvements in POTS symptoms after exercise training only to the training program because patients were encouraged to increase their daily salt and water intake and to elevate the head of the bed during sleeping at night.
- These results suggest that POTS per se is indeed a consequence of deconditioning and that carefully prescribed exercise training can be used as an effective nondrug therapy for POTS patients.
Geleijnse, Johanna M., Diederick E. Grobbee, and Albert Hofman. "Sodium and potassium intake and blood pressure change in childhood." Bmj 300.6729 (1990): 899-902.
- Dietary potassium and the dietary sodium to potassium ratio are related to the rise in blood pressure in childhood and may be important in the early pathogenesis of primary hypertension.
- Additional potassium intake may help offset any deleterious effects of sodium on blood pressure.
McLeod, Karen A. "Dizziness and syncope in adolescence." Heart 86.3 (2001): 350-354.
- Advice should be given to drink plenty (with the exception of caffeine containing drinks as they tend to dehydrate) such that the urine always looks clear. Many families now restrict the amount of salt in the diet because of concerns about future hypertension. We advise an increase in dietary salt to what might be termed a “normal” salt diet.
- Often with the above simple measures of reassurance, fluid, posture and salt, symptoms will improve significantly.
El-Sayed, H., and R. Hainsworth. "Salt supplement increases plasma volume and orthostatic tolerance in patients with unexplained syncope." Heart 75.2 (1996): 134-140.
- A double blind placebo controlled study in 20 patients and an open study in 11 of the effects of giving 120 mmol/day of sodium chloride (2700 mg sodium)
- In patients with unexplained syncope who had a relatively low salt intake administration of salt increased plasma volume and orthostatic tolerance, and in the absence of contraindications, salt is suggested as a first line of treatment.
Claydon, Victoria E., and Roger Hainsworth. "Salt supplementation improves orthostatic cerebral and peripheral vascular control in patients with syncope." Hypertension 43.4 (2004): 809-813.
- Salt supplementation improves orthostatic tolerance in many patients with posturally related syncope (PRS). This study aimed to examine whether in those patients who responded to salt loading there was also evidence of improved cerebral autoregulation and more powerful peripheral vasoconstriction during orthostasis
- Patients ... were administered 100 mmol/d (6 g) slow-release sodium chloride tablets (HK Pharma) and were reassessed after 2 months
- We had established from a previous study in our laboratory using a randomized crossover design and with placebo control that salt supplementation does significantly improve orthostatic tolerance. In this earlier study, 71% of the subjects who received salt tablets had an improvement in orthostatic tolerance, whereas only 3 of 10 subjects who received placebo showed an improvement in orthostatic tolerance. Also, in those who improved on placebo, it became apparent from urine sodium analysis that they had voluntarily increased their sodium intake during the course of the trial. Thus, we considered that we had already established that salt loading improves orthostatic tolerance in the majority of subjects
- Salt loading in PRS patients increases orthostatic tolerance and improves cerebrovascular and peripheral vascular control without affecting blood pressures. These changes are likely to contribute to the beneficial effects of salt loading in these patients.
- Salt supplementation is, in our experience, well tolerated. We have now shown that in addition to its known effect of expanding plasma volume, it also increases the vascular resistance responses to standing (and hence improves postural blood pressure control). It also improves cerebral perfusion by enhancing control of cerebral autoregulation. Perhaps equally as important, we have also demonstrated that in the patients studied, salt supplementation had no adverse effect on resting supine blood pressures.
D'Anci, Kristen E., Florence Constant, and Irwin H. Rosenberg. "Hydration and cognitive function in children." Nutrition reviews 64.10 (2006): 457-464.
- Many POTS patients are hypovolemic.
- Most experts would recommend that there be some effort to increase dietary salt in POTS patients by around 2-4g/day. Particularly symptomatic patients may benefit from as much as 6-8g sodium/day if recommended by a doctor. Initial efforts should be made through dietary salt, and if necessary salt tablet may be used if part of a treatment plan.